Ridge Regression from Scratch
Published:
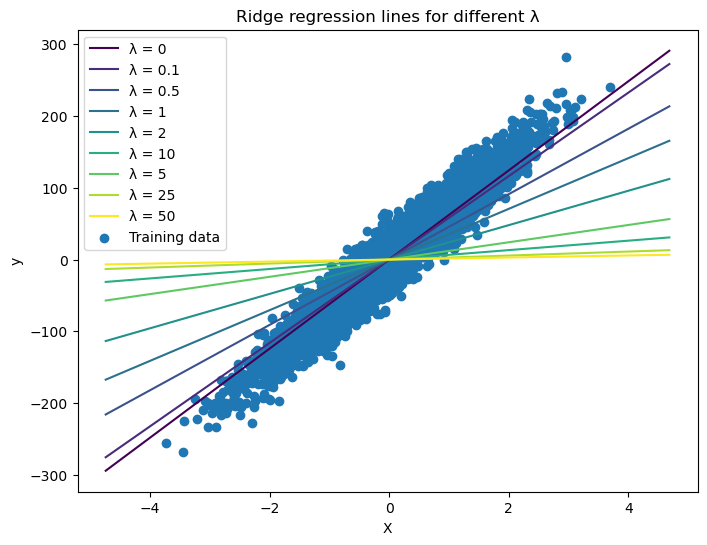
Published:

Published:
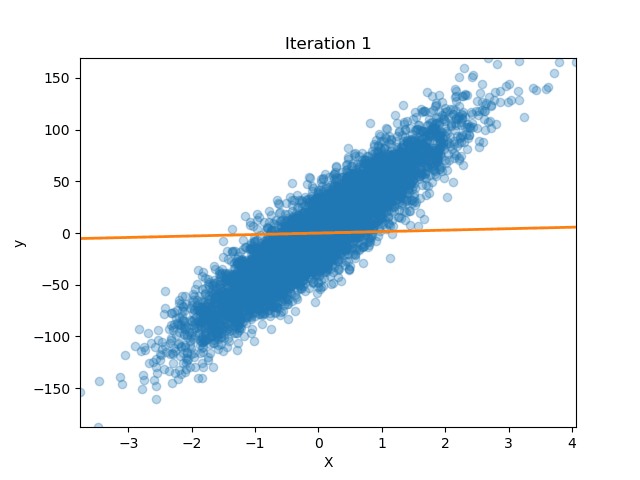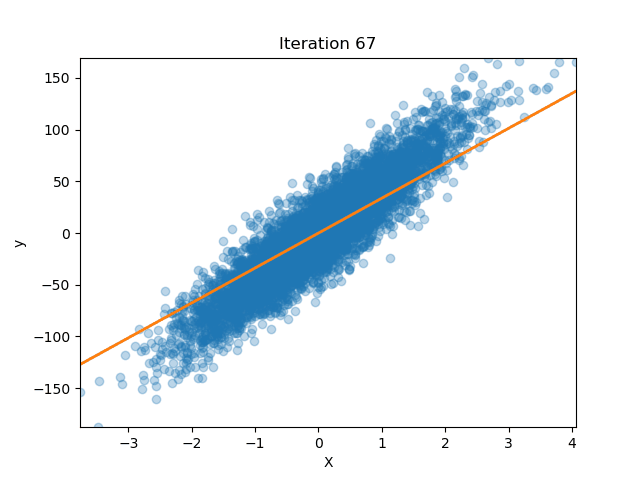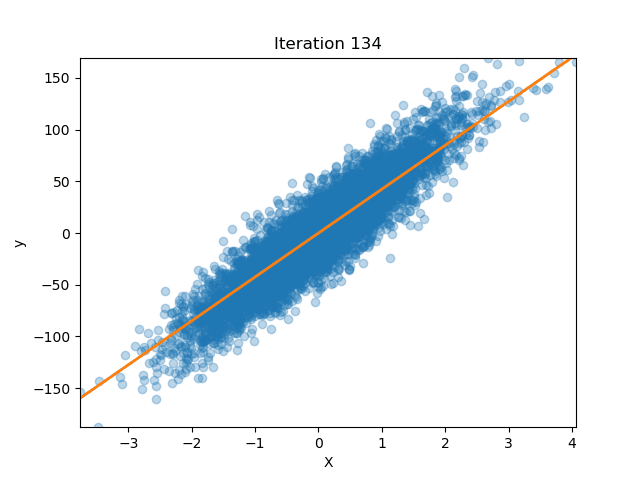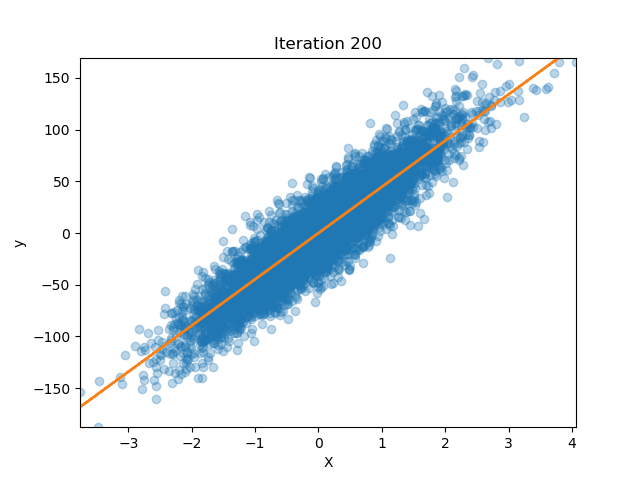
Published:
It represents the probability of observing the given data, given a particular set of parameter values. It plays a crucial role in Bayes
Published:
In very few words, Bayes is a framework for reasoning about uncertainty using probability. The core idea is that we update our beliefs about an hypothesis as we gather more and more data (evidence) .
Published:
Python provides several built-in sequence types that are implemented in C, which are divided into two categories based on how they store their contents: Container sequences and Flat sequences.
Published:
They are ‘predefined’ methods that allow you to customize the behavior of classes. Can also be referred to as “dunder” (double-underscore) methods.
Published:
Published:
Widely used for corner detection in computer
Published:
Published:
Layer Normalization is a technique in deep learning that addresses the covariate shift problem by normalizing thanks to the mean and variance calculated across features for each example.
Published:
Batch normalization has become an essential deep learning technique. Its purpose is to improve speed and add stability in the learning process by normalizing the value distribution before going into the next layer. This helps reducing the covariate shift
Published:

Published:

Published:
In machine learning (ML), a cost function (also called a loss function) is a measure of how well the model’s predictions match the actual outcomes or targets. The cost function gives a numerical value, the cost or loss that quantifies the error (or “cost”) between the predicted values and the true values The goal of training a machine learning model is to minimize this cost function by adjusting the model’s parameters.
Published:
In this post we will review the very basics of Recurrent Neural Networks. What are they, the math behind it and how they can be used.
Published:
Cross-entropy is one of many possible cost function that we might consider choosing for our model and is typically used in Categorical Classification. This means, a model that aims to predict whether our input data is one in a finite size possible classes.
Published:
Published:
In machine learning (ML), a cost function (also called a loss function) is a measure of how well the model’s predictions match the actual outcomes or targets. The cost function gives a numerical value, the cost or loss that quantifies the error (or “cost”) between the predicted values and the true values The goal of training a machine learning model is to minimize this cost function by adjusting the model’s parameters.
Published:
In this post we will review the very basics of Recurrent Neural Networks. What are they, the math behind it and how they can be used.
Published:
Cross-entropy is one of many possible cost function that we might consider choosing for our model and is typically used in Categorical Classification. This means, a model that aims to predict whether our input data is one in a finite size possible classes.
Published:
Published:
It represents the probability of observing the given data, given a particular set of parameter values. It plays a crucial role in Bayes
Published:
In very few words, Bayes is a framework for reasoning about uncertainty using probability. The core idea is that we update our beliefs about an hypothesis as we gather more and more data (evidence) .
Published:
The general process of TMAP looks like this:
Published:

Published:

Published:
Unittesting for any serious project is mandatory, not optional. It’s a good negative indicator -i.e. it points out poor-quality code with relatively high accuracy-. If the code is hard to unit test, it’s a strong sing that the code needs improvement.
Published:
Python provides several built-in sequence types that are implemented in C, which are divided into two categories based on how they store their contents: Container sequences and Flat sequences.
Published:
They are ‘predefined’ methods that allow you to customize the behavior of classes. Can also be referred to as “dunder” (double-underscore) methods.
Published:
Published:
Layer Normalization is a technique in deep learning that addresses the covariate shift problem by normalizing thanks to the mean and variance calculated across features for each example.
Published:
Batch normalization has become an essential deep learning technique. Its purpose is to improve speed and add stability in the learning process by normalizing the value distribution before going into the next layer. This helps reducing the covariate shift
Published:
Let’s say we have a dataset of 10 molecules (A through J), and we want to construct a 3-NN graph (k=3) where k indicates the number of neighbours.
Published:
The general process of TMAP looks like this:
Published:
Locality-sensitive hashing or LSH, allows us to focus on pairs that are likely to be similar, instead of having to look at all pairs possible. It reduces therefore the amount of computational time required by a brute force approach.
Published:
TL;DR: MinHashing is a way to reduce the dimensionality of fingerprints. Instead of comparing 512-bit vectors directly -these are the vectors that we obtain after the fingerprint is applied to a SMILES format molecule-, MinHash reduces these vectors to smaller hashes that preserve similarity between molecules.
Published:
TL;DR: MinHashing is a way to reduce the dimensionality of fingerprints. Instead of comparing 512-bit vectors directly -these are the vectors that we obtain after the fingerprint is applied to a SMILES format molecule-, MinHash reduces these vectors to smaller hashes that preserve similarity between molecules.
Published:
TL;DR: MinHashing is a way to reduce the dimensionality of fingerprints. Instead of comparing 512-bit vectors directly -these are the vectors that we obtain after the fingerprint is applied to a SMILES format molecule-, MinHash reduces these vectors to smaller hashes that preserve similarity between molecules.